How to cure eczema easily
An Insight into Eczema; Symptoms, Triggers & Treatments
Eczema is a condition found in 1 in 10 individuals around the globe. It usually appears at an early age in children but can also appear in later stages of a person’s life. Eczema comes along with many hassles but following the right instructions and developing a strict routine can definitely reduce its effects and even make it disappear for some time. In this article, “How to cure eczema easily?” we will look into the course of identifying the symptoms of eczema and take the edge off its effects through different precautions and treatments.
What is eczema?
Eczema is a skin condition that often arises during early childhood and may disappear and reappear every now and then. It refers to various skin conditions, many of them relating to allergy. It is a disease that weakens the skin’s barrier which makes it vulnerable to different types of skin infections.
Is Eczema contagious?
Eczema is often misunderstood and confused as a contagious disease but studies have proved that it is non-contagious and cannot be transferred to others by any means of physical contact. Rather it is referred to as a genetic condition passed on by the parents to the child.
Types of eczema, their causes, and symptoms
There are many different types of eczema. Some of them are listed below:
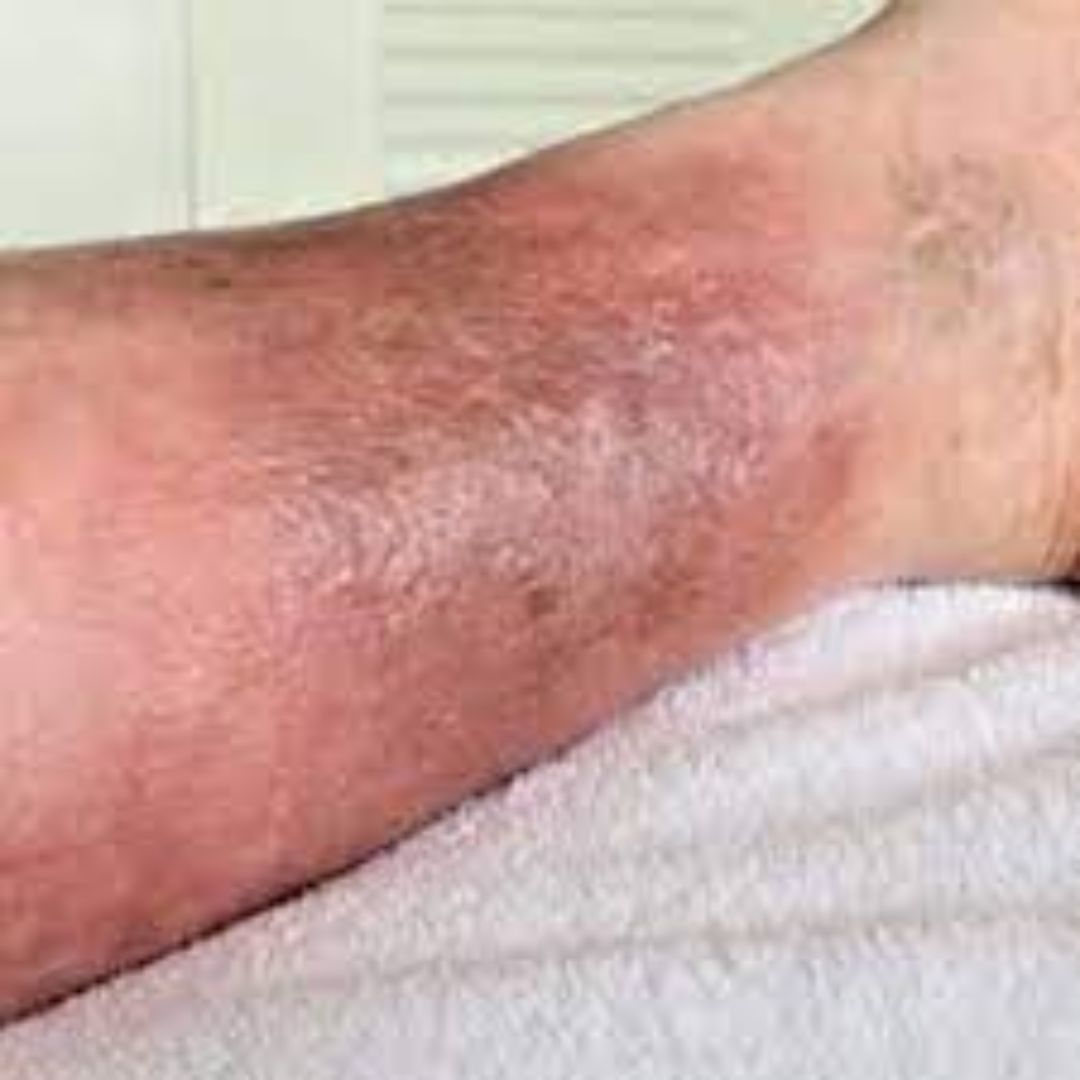
1. STASIS DERMATITIS
Stasis dermatitis is a condition that often appears around the lower legs or ankles. It may appear in other areas of the body but that is found to be extremely rare. Stasis dermatitis is also referred to as gravitational or venous eczema and mostly arise due to aging.
Causes:
Stasis dermatitis is a type of eczema that is a result of poor blood flow to the lower legs. The poor blood flow may develop due to old age as the valves situated in the lower legs become weak and allow fluid to escape and deposit itself in the legs causing them to swell. This condition is not only restricted to old age but can also develop due to several other reasons such as:
- Leg injury
- Clotting of blood
- A serious heart or kidney condition
Symptoms:
- Swelling
- Itching
- Scaling
- Hyperpigmentation
- Skin is sensitive to touch
2.CONTACT DERMATITIS
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema that turns up when a person comes into contact with a surface with a certain substance present on it which causes irritation on the affected skin or an allergic reaction. Contact dermatitis is further divided into two branches known as:
IRRITANT CONTACT DERMATITIS(NON-ALLERGIC):
Causes:
It is caused due to exposure to irritating substances that depends on the person who is affected. Some of the common irritants are:
- Soap
- Detergents
- Acid or other solvents
- Bleach
Symptoms:
A red itchy rash appears when a person comes into contact with an irritating substance due to the cells in the protective skin layer being damaged. Reaction depends on the amount of irritant and time a person is exposed to. Stronger irritants make people react immediately with a single exposure in a shorter period of time while weaker irritants make them react after multiple frequent exposures or after several hours.
ALLERGIC CONTACT DERMATITIS(ALLERGIC):
Causes:
It is caused due to a person developing an allergy to a particular substance before coming into contact with it. An immune or allergic reaction takes place when the allergy is triggered. Some of the common allergens are:
- Nickel in jewelry
- Poison ivy
- Chemicals in skin care products
- Chemicals in fragrances
- Latex
- Cosmetics
Symptoms:
An itchy rash similar to that of irritant contact dermatitis but being triggered by an allergen. Mostly only the area that came into contact with the allergen reacts.
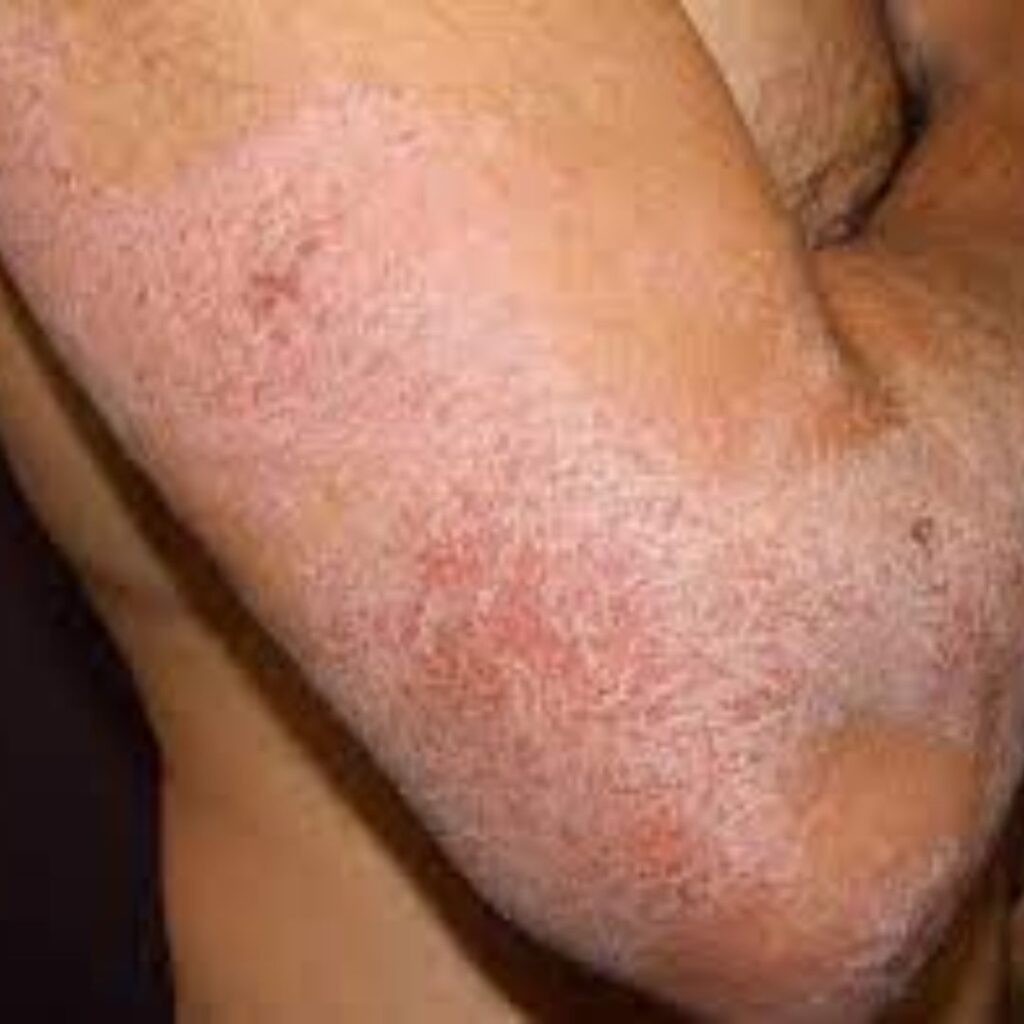
3.ATOPIC DERMATITIS:
Atopic dermatitis is a condition that affects the skin’s barrier function and weakens it and allows bacteria to enter. This is the most commonly found eczema which mostly appears around the toddler phase but can start around any age. After appearing atopic dermatitis affects a person their whole life but can disappear for some time with proper treatment. It occurs anywhere where there is skin but is commonly found in areas where the skin flexes such as behind the elbows and knees. People who have hay fever or asthma have more chances to get atopic dermatitis.
Causes:
Atopic dermatitis is mostly a genetic condition that weakens the skin barrier which makes it more prone to bacteria. People that are victims to hay fever or asthma have more chances to develop this condition. It is often triggered by certain things that vary with every individual. But some common triggers are:
- Heat and sweat
- Dry skin
- Certain fragrances and irritant chemicals
- Rough fabric
- Certain foods
Symptoms:
Atopic dermatitis often appears in areas around the body parts that bend such as the neck, behind the knees or elbows. The symptoms often include dry, cracked skin, red, brown or purple rashes. It also includes non-stop itchiness. Severe states include bumps that ooze and bleed.
Easy Treatments for Each Type of Eczema
FOR STASIS DERMATITIS:
To help with the swelling, elevation and compression is recommended. The legs should be elevated above the heart and compression bandages should be wrapped around the swollen areas. Salty foods should be limited. Antibiotics can help with the itchiness and pain but a dermatologist’s consent is required. Hyperpigmentation is difficult to get rid of but it can disappear with time. Standing or sitting on your legs for a long period of time must be avoided. Stasis dermatitis may be a condition that sticks throughout your entire life.
FOR CONTACT DERMATITIS
To treat contact dermatitis, the allergens and irritants must first be identified through tests and observations. A dermatologist should be visited for proper diagnosis. After identification try to avoid the allergens and irritants that trigger your contact dermatitis. On the advice of your dermatologist, use ointments and steroids to help with the flare ups. Avoid using moisturizers and soaps that contain fragrances. If a part of your body comes into contact with an allergen, immediately wash that area with cold water. Apply a damp cloth with cold water on the rashes to reduce inflammation. Contact dermatitis can go away if proper treatments are used and known allergens and irritants are avoided completely.
FOR ATOPIC DERMATITIS
On the recommendation of a dermatologist, take drugs and certain ointments to reduce itchiness and pain. Avoid scratching at all costs and trim your nails for further help. Avoid staying in heated areas and wear light fabric clothes that are breathable for your skin. Take daily showers and moisturize on a daily basis. Natural oils can be used with the daily baths to treat dry skin. Changes in your diet must be made if certain food triggers your eczema. Furthermore, reducing stress and anxiety levels can also help. You can’t get rid of atopic dermatitis but symptoms can improve overtime.
CONCLUSION:
Eczema is a really common disease found all around the world, regardless of age. As of right now, there is no proper and authentic cure for eczema. But eczema can be easily treated and improved as time goes on but only if a strict routine is followed through. Mild eczema can be treated with home remedies. Severe cases require a dermatologist, medical procedures, and medications.
Read Also: Is It Ok To Use Niacinamide With Retinol Together
FAQs
q1) What causes Eczema fast?
Eczema can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, immune system dysfunction, environmental triggers like allergens or irritants, and disruptions in the skin barrier function.
Q2) How to stop Eczema itching immediately?
To stop eczema itching immediately, you can try:
1 Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area to numb the itch.
2 Using over-the-counter anti-itch creams or ointments containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or calamine.
3 Taking a lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda to soothe the skin.
4 Moisturizing the affected area with a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and prevent further itching.
5 Avoiding scratching, as it can further irritate the skin and lead to more itching and inflammation.
If itching persists or worsens, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment options.
Q3) how quickly can eczema heal?
The healing time for eczema varies, but it can take anywhere from a couple of weeks to several months or longer.